
Time:2022-01-06 Read:1394
Polarized beam intensity ratio analyzer (PBA), which is a basic optical element to detect the polarization of the incident light, plays a critical role in the photonics system. Over the past decades, several PBAs has been reported. There are bulk-type structures, grating-type structures, fiber-type structures, and waveguide-type structures. As is well known, the conventional bulk-type PBA is popular in free-space optical signal processing. However, the cumbersome is a significant disadvantage of traditional bulk-type PBA, indicating that it is infeasible for application and integration. Therefore, the PBA based-on grating-type has been produced in recent years, which can offer desirable performance of polarization modulation owning to its light weight and small size. Nevertheless, the grating-type PBA is hard to be applied to the field of communications due to high loss and harsh process requirements. In general, the fiber-type PBA is widely utilized in communications. It has excellent transmission characteristics that makes it convenient for communications. However, it is difficult to be designed and fabricated with highly sensitive of detection. Thus, producing an especially high-performance PBA suiting for large-scale application in the integrated system is a fiercely desire.
Actually, the waveguide technology provides a chance due to the distinct advantages, such as small size, low weight, stable, reliable performance, and easy integration. It is of great interests to implement the PBA by utilizing the waveguide. The double metal-cladding waveguide (DMCW), can excite the ultrahigh-order guided modes (UOMs) which have many outstanding properties, for example, high modes density in guided layer, small propagation constant of light, free-space coupling into guided layer at small incident angle, highly sensitive detection of weakly refractive index and so on. Based on these unique properties, the DMCW has been used to many achievements in sensors and actuators.
We demonstrate a new type PBA based on the DMCW, which achieves sensitive detection of different orthogonal polarization intensity ratios due to distinguishing the TE/TM polarization via the coupling efficiency of light in waveguide. The DMCW has three-layer structure and the middle-guided layer is a uniaxial negative crystal lithium niobate (LN) which has different refractive indices for orthogonal eigen-polarizations, the ordinary o and extraordinary e states. In this DMCW, TE and TM polarization resonate at many different coupling angles. Hence, when the incident light meets the resonance angle of one polarization mode, it will be fully coupled into the guided layer of DMCW, and the other polarization mode will be completely reflected. Meanwhile, the TE/TM polarization light will excite different modes in DMCW at corresponding incident angle which is coupling angle, respectively. In addition, the difference coupling angle between TE and TM is only 0.01° that can be distinguished by DMCW. Moreover, our PBA is able to support large wavelength range and wide-angle extent.
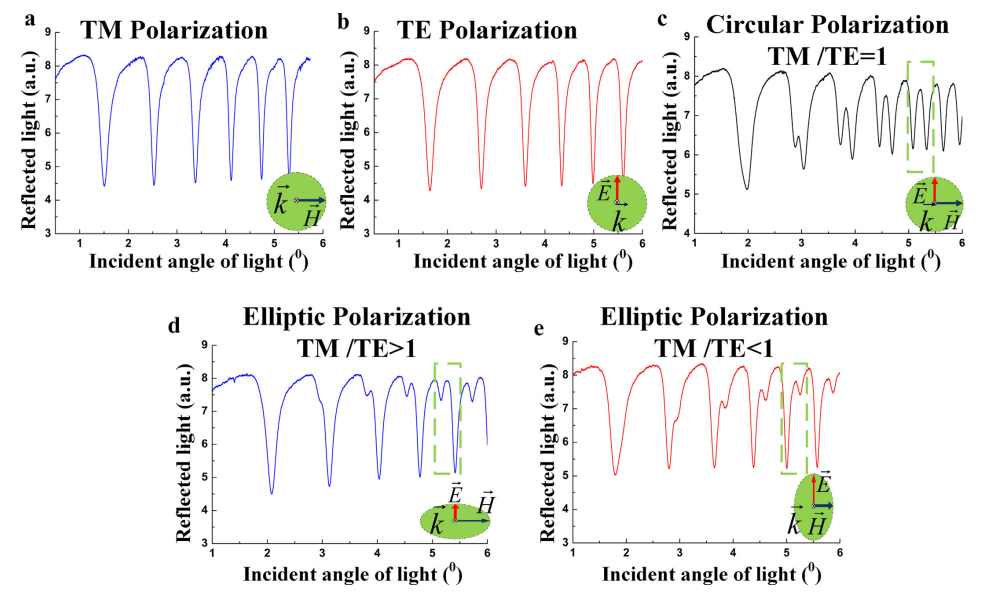
Figure. Experimental verification of the proposed PAB method with distinct polarized beams at the wavelength of 632.8nm.
The research was published in “Hongrui Shan, Qiheng Wei, Hailang Dai, and Xianfeng Chen, Sensitive detection of orthogonal polarization intensity ratio via double metal-cladding waveguide, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 151, 106920 (2022)”
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0143816621003894?dgcid=coauthor